Almost every '90s kid will recall that they or their parents had those small phones that allowed around 160 characters of text messages. These phones used the 1G mobile network. 1G refers to a first-generation mobile network. Communication technology has evolved since then and we have seen 2G, 3G, and 4G networks. Now, we are in for 5G, the new and fast generation of network. So, what is 5G? How does it work?
What is 5G?
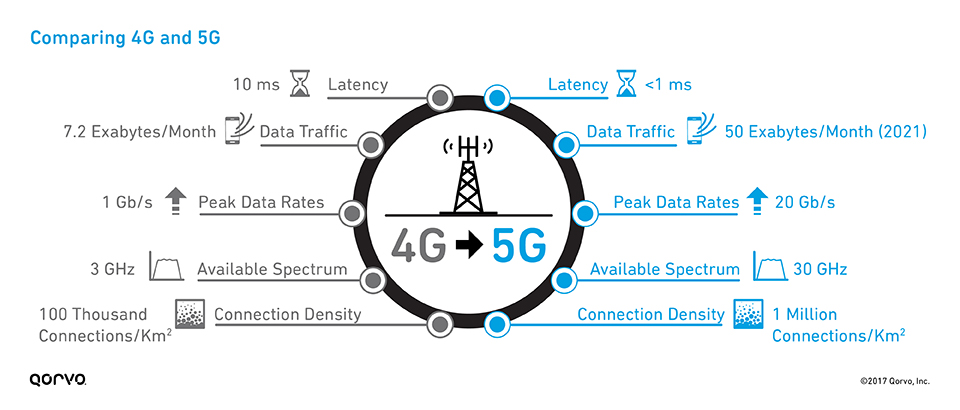
5G is the fifth generation of mobile networks. 5G is said to be a cloud-based mobile network. This network has much higher data transfer speeds compared to previous generations, which is obvious. The data transfer speed of 5G can go up to 18 Gbps. These high speeds would be really useful in large events where there is a lot of stress on the network bandwidth. 5G will have a much lower network lag and significantly impact gaming and cloud services. This network is said to enhance the capabilities of self driving cars, Internet of Things (IoT), and online immersive education.
photo by qorvo.com
How does it work?
According to Wikipedia, "5G networks are digital cellular networks, for which the service area is divided into small geographical cells. The 5G wireless devices in a cell communicate by radio waves with a local antenna array and low power automated transceiver (transmitter and receiver) in the cell, over frequency channels assigned by the transceiver from a pool of frequencies that are reused in other cells. The local antennas are connected to transmission electronics connected to switching centers in the telephone network and routers for Internet access by a high-bandwidth optical fiber or wireless backhaul connections. As in other cell networks, a mobile device moving from one cell to another is automatically handed off seamlessly to the current cell. 5G can support up to a million devices per square kilometer, while 4G supports only one-tenth of that capacity. The new 5G wireless devices also have 4G LTE capability, as the new networks use 4G for initially establishing the connection with the cell, as well as in locations where 5G access is not available." The above sentence summarizes how this mobile network works. Usually, when you use your phone to make a call or send a message, the network provider assigns a specific frequency to you, which then is used by the mobile towers to send the information to the receiver. And, to achieve higher data transfer speeds, we need to use high energy frequencies. But, the problem with higher frequency waves is that they are attenuated very easily. Attenuation means weakening of the radio signal due to environmental factors or constructions. Attenuation of waves leads to a decrease in the range of mobile towers. So, to support 5G, there would be a need of extra transmission towers for any given area. 5G increases network speed by dividing information into chunks and then using a range of frequencies to transfer this information to the receiver.

credits: qorvo.com
Advantages of 5G:
1. High data transfer speeds.
5G is said to provide a maximum data transfer speed of 18 Gigabytes per second. This means that if it takes an hour to download a movie on your phone using 4G, it would take just a few seconds for 5G. Self-driving cars would be highly benefitted from high network speed because that will allow them to make faster communication with neighboring cars. High speed will also boost the usability of Internet of Things(IoT).
2. Small size of receivers:
5G uses millimeter waves, which have small wavelengths than those used for previous generation mobile networks. A decrease in wavelength means a reduction in receiver size. So, 5G towers would be small compared to 4G transmission towers.
3. Convergence of Wifi and cellular network:
One expected benefit of the transition to 5G is the convergence of multiple networking functions to achieve cost, power, and complexity reductions. LTE has targeted convergence with Wi-Fi band/technology via various efforts, such as License Assisted Access(LAA; 5G signal in unlicensed frequency bands that are also used by Wi-Fi) and LTE-WLAN Aggregation (LWA; convergence with Wi-Fi Radio), but the differing capabilities of cellular and Wi-Fi have limited the scope of convergence. However, significant improvement in cellular performance specifications in 5G, combined with migration from Distributed Radio Access Network (D-RAN) to Cloud- or Centralized-RAN (C-RAN) and rollout of cellular small cells can potentially narrow the gap between Wi-Fi and cellular networks in dense and indoor deployments. Radio convergence could result in sharing ranging from the aggregation of cellular and Wi-Fi channels to the use of a single silicon device for multiple radio access technologies.
4. It is safe:
It has been a hot topic of debate whether 5G is safe for us or not. But, there is no reason 5G will harm us in any way because the energy in the waves used for transferring information through 5G is less than that present in visible light. And clearly, visible light does not hurt us and is safe. So, obviously, 5G is a safe technology for us.
So, that's all about 5G. What do you think about this new generation of networks? Let me know your thoughts in the comments section. That would be helpful for me.
Also read:
Thanks for reading.

Post a Comment